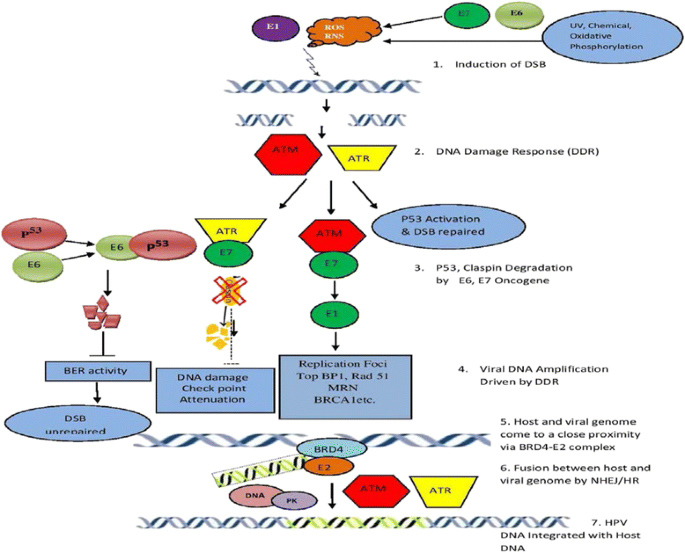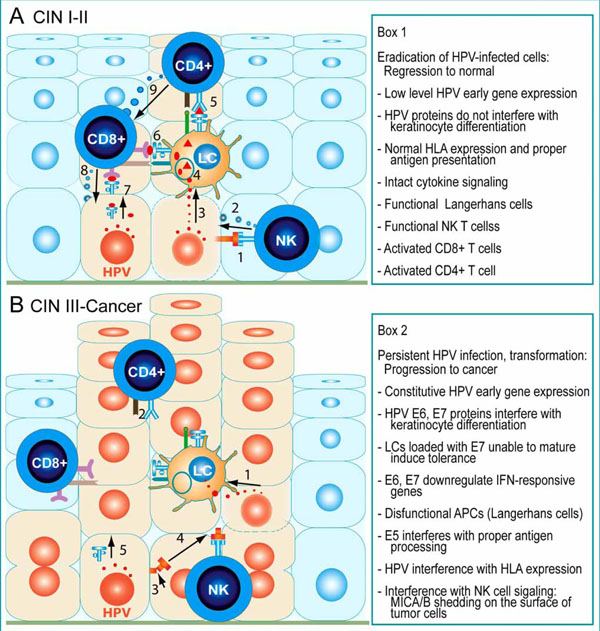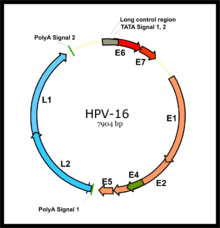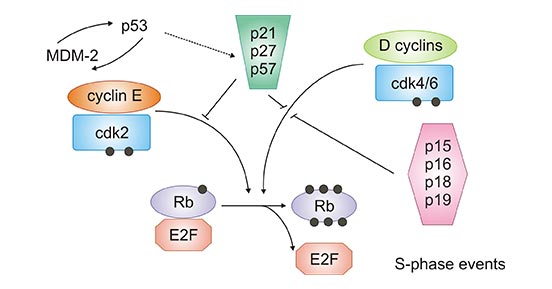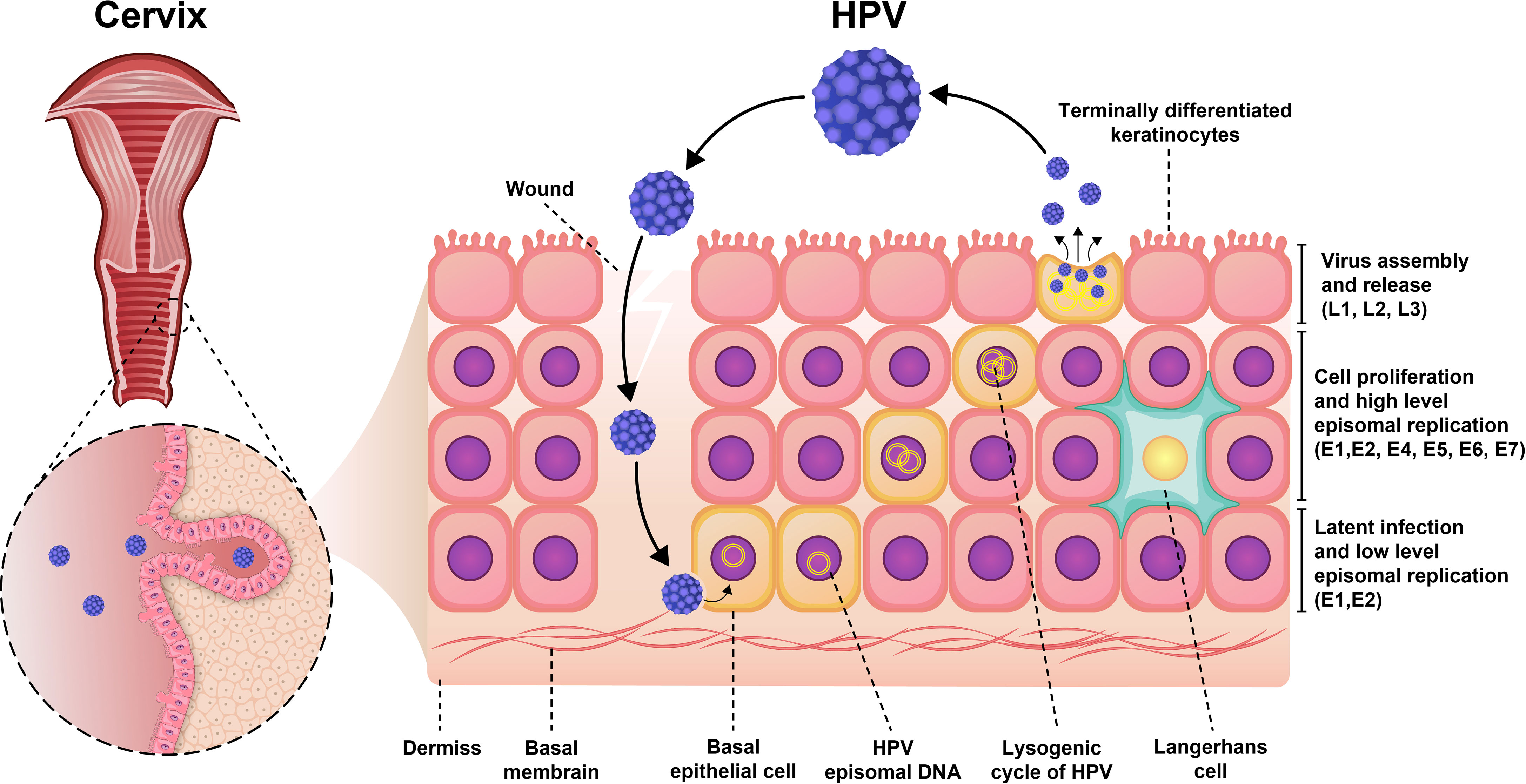
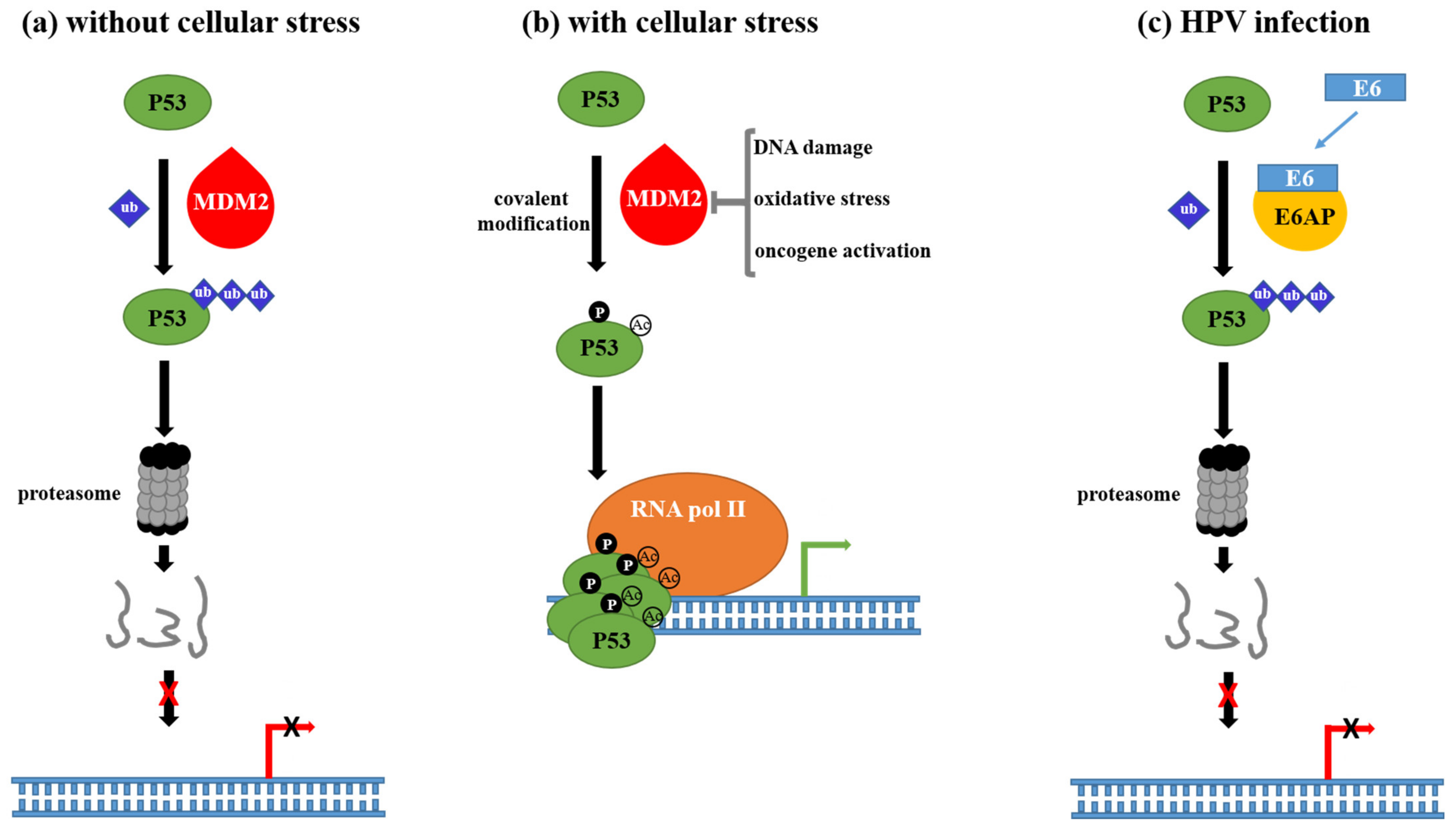
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Molecular mechanisms in progression of HPV-associated cervical carcinogenesis | Journal of Biomedical Science | Full Text

A Human Papillomavirus-Independent Cervical Cancer Animal Model Reveals Unconventional Mechanisms of Cervical Carcinogenesis - ScienceDirect
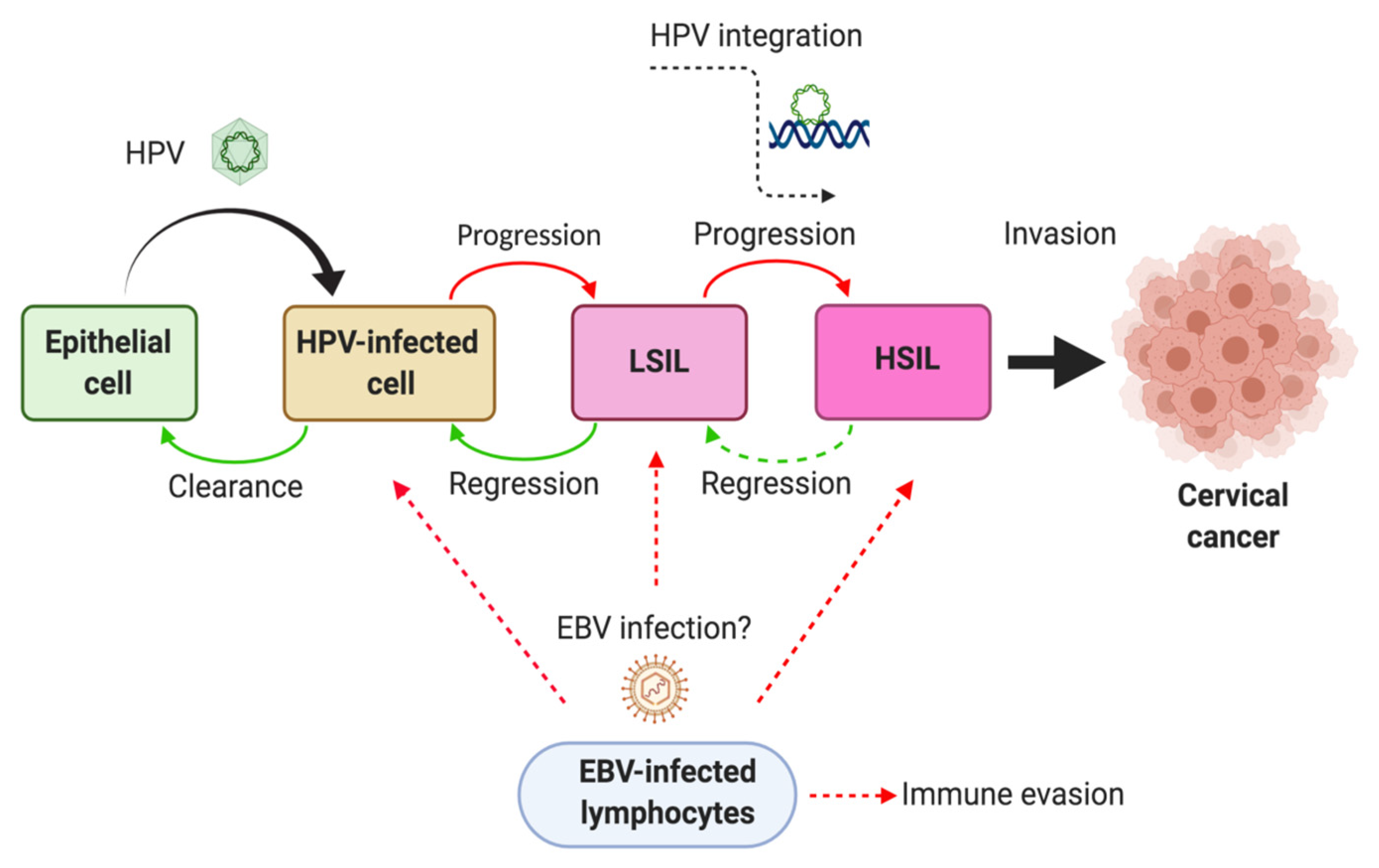
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Role of Epstein-Barr Virus and Human Papillomavirus Coinfection in Cervical Cancer: Epidemiology, Mechanisms and Perspectives

Mechanism of action of anti-programmedcell-death-protein-1 antibody in... | Download Scientific Diagram
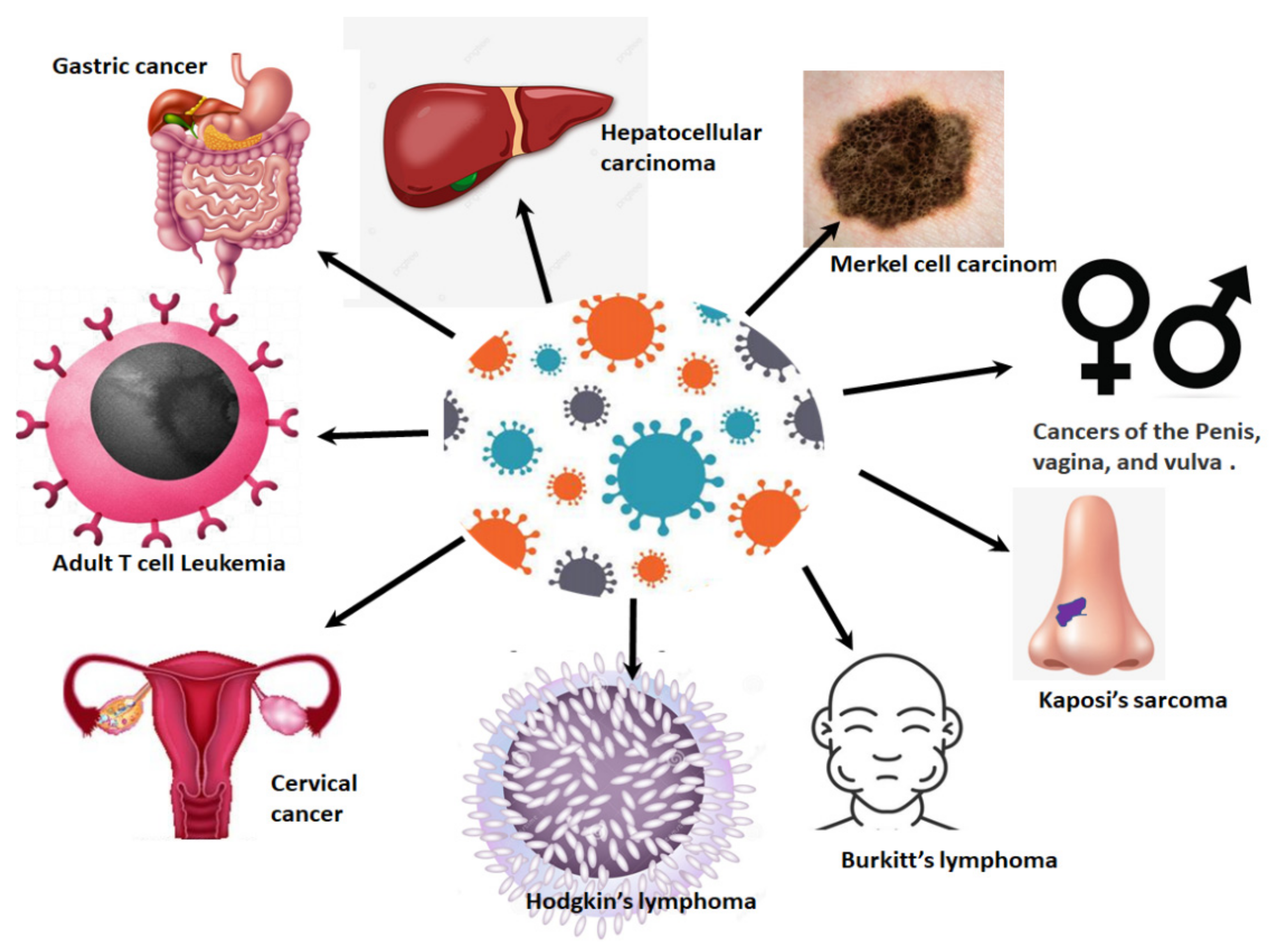
IJMS | Free Full-Text | The Catastrophic HPV/HIV Dual Viral Oncogenomics in Concert with Dysregulated Alternative Splicing in Cervical Cancer

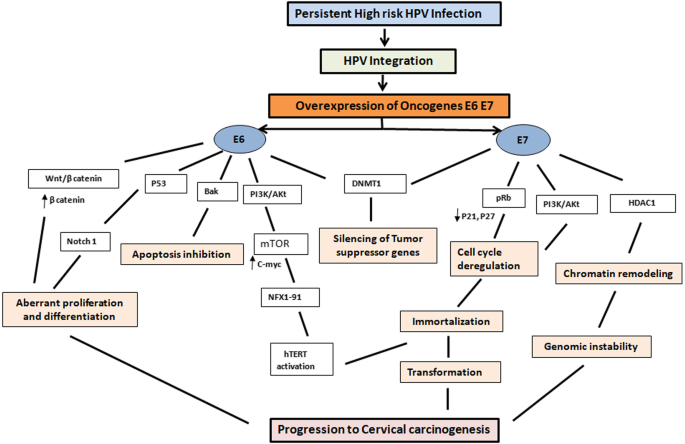
Basic mechanisms of high‐risk human papillomavirus‐induced carcinogenesis: Roles of E6 and E7 proteins - Narisawa‐Saito - 2007 - Cancer Science - Wiley Online Library
Cells | Free Full-Text | The Interaction of Human Papillomavirus Infection and Prostaglandin E2 Signaling in Carcinogenesis: A Focus on Cervical Cancer Therapeutics
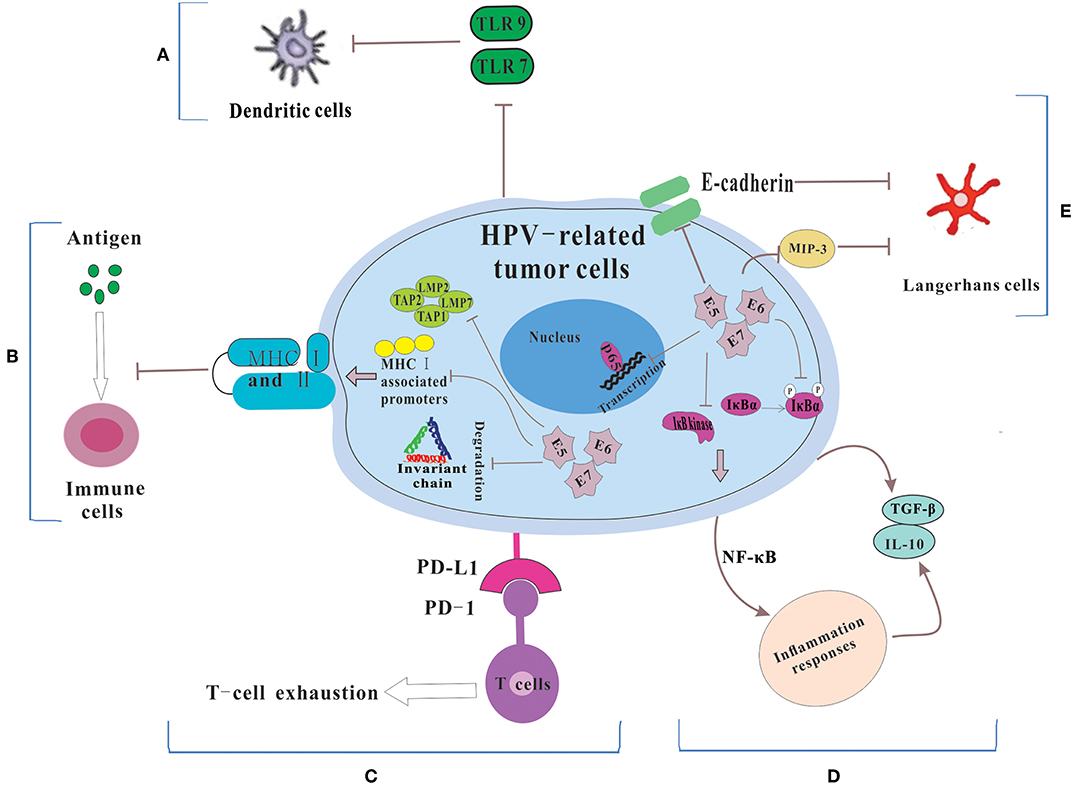
Frontiers | The Double-Edged Sword—How Human Papillomaviruses Interact With Immunity in Head and Neck Cancer
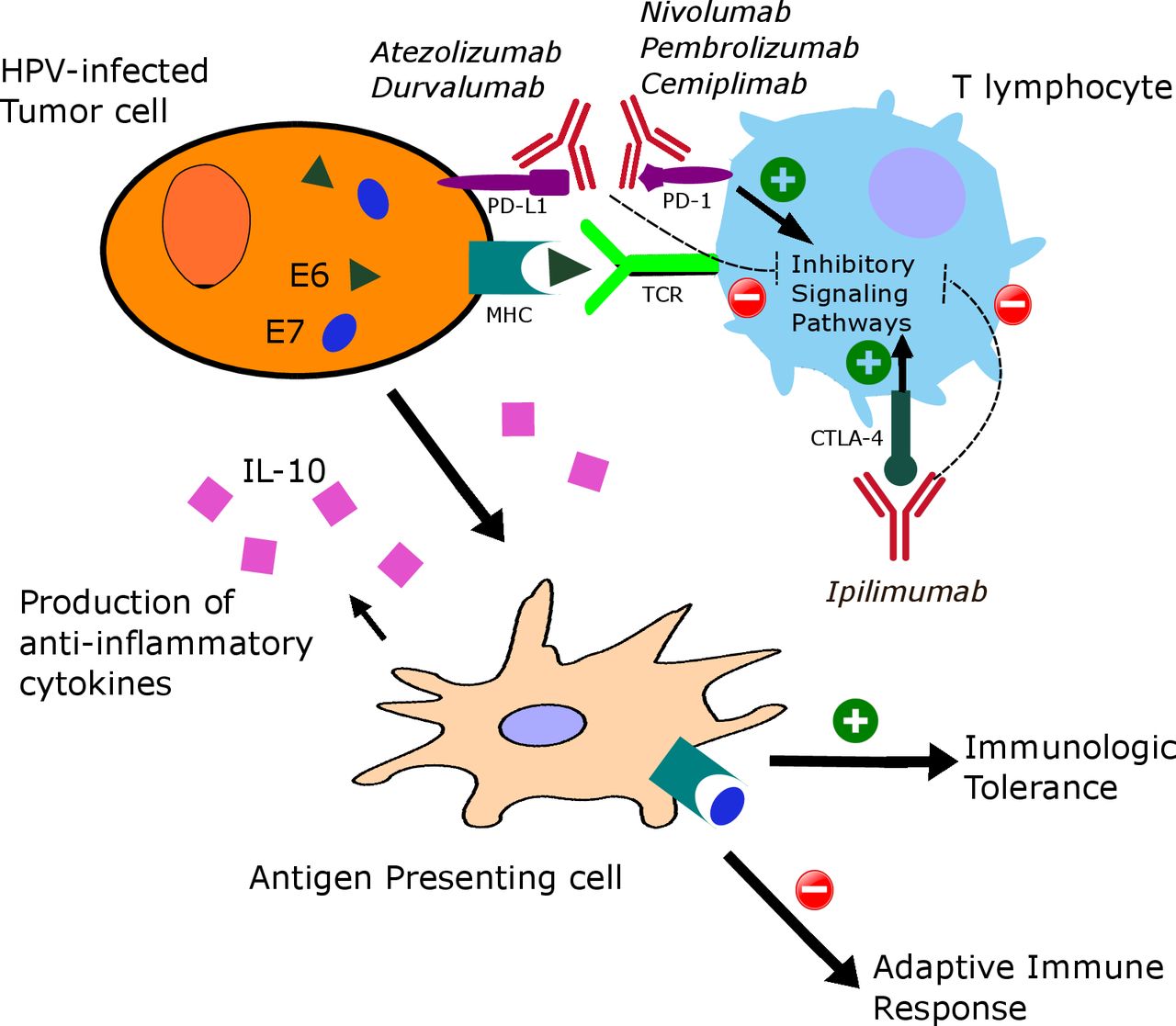
Advances in immunotherapy for cervical cancer: recent developments and future directions | International Journal of Gynecologic Cancer

Gene knock-out chain reaction enables high disruption efficiency of HPV18 E6/E7 genes in cervical cancer cells: Molecular Therapy - Oncolytics

Basic mechanisms of high‐risk human papillomavirus‐induced carcinogenesis: Roles of E6 and E7 proteins - Narisawa‐Saito - 2007 - Cancer Science - Wiley Online Library

Basic mechanisms of high‐risk human papillomavirus‐induced carcinogenesis: Roles of E6 and E7 proteins - Narisawa‐Saito - 2007 - Cancer Science - Wiley Online Library
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Molecular mechanisms in progression of HPV-associated cervical carcinogenesis | Journal of Biomedical Science | Full Text
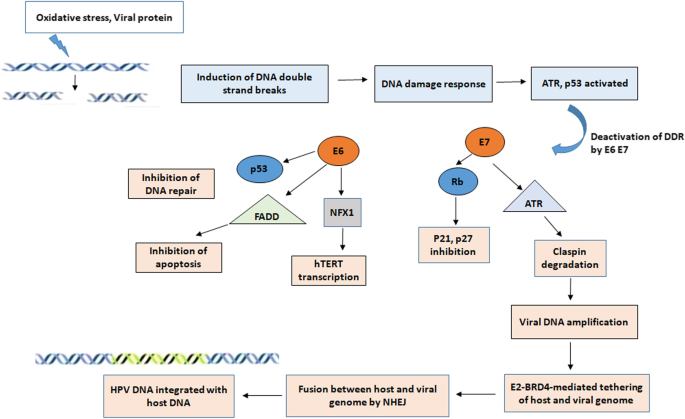
![PDF] Mechanisms of virus immune evasion lead to development from chronic inflammation to cancer formation associated with human papillomavirus infection | Semantic Scholar PDF] Mechanisms of virus immune evasion lead to development from chronic inflammation to cancer formation associated with human papillomavirus infection | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/ce654eb6de3f5659147d13de97e9be8fc68ce97b/4-Figure3-1.png)
PDF] Mechanisms of virus immune evasion lead to development from chronic inflammation to cancer formation associated with human papillomavirus infection | Semantic Scholar
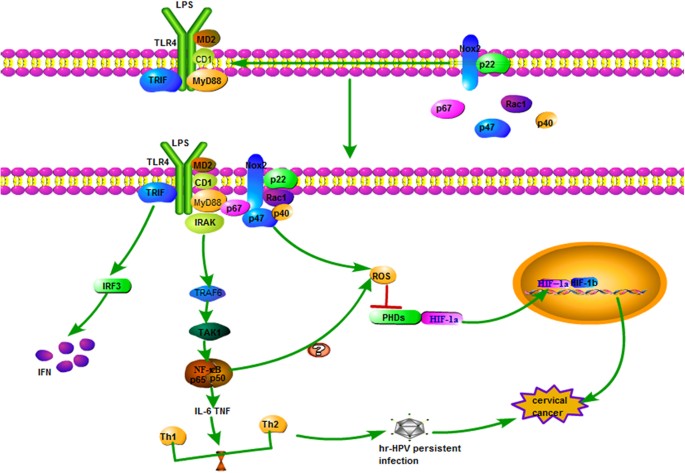
The role of TLRs in cervical cancer with HPV infection: a review | Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy

Human Papillomavirus Induced Cervical and Oropharyngeal Cancers: From Mechanisms to Potential Immuno-therapeutic Strategies | Bentham Science

Deciphering the complex interplay between microbiota, HPV, inflammation and cancer through cervicovaginal metabolic profiling - eBioMedicine